Abstract
Entrepreneurship in the international business has become one central element that has helped multinational organisations attain sustainability, growth and economic stability. Therefore, this research work aims to understand the impact of entrepreneurship in the Global Business scenario. Apart from this, the research work would discuss a clear indication of different aspects of entrepreneurship stitches value creation and risk tolerance to understand its future impact and the current assessment of the multinational organisations at the same time. The secondary research method is to identify where the scholarly articles and journals are critically evaluated to understand the impact of entrepreneurship and its practices in international businesses. At the same time, value creation and risk tolerance are separately discussed, two adjacent to the research objectives. The findings have manifested that entrepreneurship has become one of the significant elements of international business success. Value creation needs to be conducted while considering other effects of entrepreneurship skills. On the other hand, the risk tolerance in specific multinational organisations has created several benefits for the company to sustain for a more extended period, which is an excellent example of efficient entrepreneurship.
Chapter 1: Introduction
Background of the research
The current international business operations of the international organisations have become so much more complex and more problematic as it requires a continuous enhancement of the leadership qualities and Entrepreneurship practices. The vital needs of the business scenario in the changing environment are continuously demanding better entrepreneurship skills to be practised (Agostino et al. 2014). This has created a situation where entrepreneurs need to focus on managing the international business environment. As it is a priority, the persistence of multiple leaders like Steve Jobs, Elon Musk, and the contemporary other leaders have manifested the importance of entrepreneurship practices and skills to expand a business and maintain a competitive advantage. Entrepreneurship in international business can be defined as an opportunity which can be utilised to create resources and implement those resources concerning the business scenario to innovate new ideas and implement new facilities for the target consumers (Arshed et al., 2021). In other words, entrepreneurship can help businesses think critically while identifying the available opportunities to connect with the market needs and develop new creative ideas. The impact of entrepreneurship is essential in international business as entrepreneurs’ natural behaviour helps orient the business. It also helps move toward discovering the current status of those future strategies that can be developed based on the analysis.
Global business refers to the multinational companies operating in several countries together with their production base in the domestic region and their subsidiaries in other foreign countries around the globe. With a massive increment in international businesses in the past few decades, most new companies are born global companies. These interdependent and integrated international businesses are complex, ambiguous, volatile, and highly risky. An increasing requirement is an agreement to follow and implement a robust, robust and super flexible entrepreneurship style. The challenges and problems they face are critical and vital to having a relaxed and high-risk tolerating attitude and entrepreneurship style. Several issues like distance and resources may create a bigger problem for the entrepreneur to successfully operate and manage global businesses (Augustyniak, 2017). Thus, the value creation strategy should be implemented and given vital importance by innovating new products and services of more perceived value and satisfying the demand and needs of customers across several countries. One product in a country may meet and fulfil the condition of the customers in that country. Still, it may not be able to satisfy the need of the customers in another country as they have different wants and desires for the same product. Thus, producing a unified product with perceived value across all countries becomes important using the value creation strategy. These global business activities always encompass high risks and uncertainty (Burgel and Murray, 2000). Thus, an entrepreneur to successfully manage international businesses needs to have the trait to tolerate high stakes and must have the courage to push through delays, always create value, and give importance to value creation in every aspect of global business processes.
Global business refers to the production of goods and services. Their supplies cross country borders and across various countries, generally with their production base in the domestic region and their subsidiaries in other nations. Global business encompasses the full range of cross-border exchanges of goods, services and even resources between two or more countries and operates around the globe. This interdependent and integrated global business creates more significant opportunities for successful international trade and growth and is a multinational corporation (MNC). These multinational businesses are highly complex and full of ambiguity and uncertainty, and are always of high risk to manage. Thus, these multinational corporations need robust, efficient, and solid management that can work in-depth and manage the business in detail as Amazon does. Therefore, as a result, the entrepreneur has the prime duty and task to manage this vast uncertain and risky global business efficiently and effectively. An entrepreneur needs to have several personality traits and skills to handle such a huge task. To successfully manage a global business, an entrepreneur should be brave and persistent. Passion, self-belief, high motivation and courage are some of the personal traits of an entrepreneur needed to be successful on the global stage (Chaudhry et al. 2019). Assessing, minimising, and having a high tolerance towards risks is vital and imperative for an entrepreneur managing global international business. Steve Jobs, Bill Gates, Richard Branson, and Elon Musk are some of the successful entrepreneurs who all had these traits and were persistent in their actions. They all believe that persistence in your actions, high tolerance of risks, and innovative value creations with self-belief in trusting your works and abilities are critical to a successful entrepreneur for global business. This stresses that courage and high tolerance to face acute difficulties and complex risks are essential aspects of an entrepreneur. Suppose an entrepreneur knows the goals to be achieved and the best optimal and proper ways to achieve them. In that case, it becomes easier to align the several business processes according to it and thus, success can be achieved by implementing them effectively. Therefore, assessing risks and high tolerance of risks in this uncertain and highly volatile global market is very important for an entrepreneur. In these unsure international risky businesses, the importance of value creation through innovations of new products and services becomes more critical (Crick et al. 2018). The entrepreneur’s design of value through a unified, consistent, quality product or service to be supplied across various nations generates a substantial competitive advantage. It makes it competent in the global market.
Along with this, it can create value with the services and products for the consumer market to enhance competitive advantage at the same time. Advantages of entrepreneurship in international business: it helps increase organisational revenue and decrease competition (Dodo et al. 2017). Apart from this, entrepreneurship skills and competencies among the leaders can also create an easier class cash flow management what the organisation to reduce its complex operations and provide an opportunity to strengthen its facilities to deal with this in future.
Research problem
The research problem can be identified in terms of focusing on the various aspects like
- The lack of proper entrepreneurship skills among the contemporary leader,
- International businesses too faced difficulties with increased loss of revenue and profit,
- Placing the business into a hard-core competition,
- Lack of strategic application of the movements to help businesses elevate those situations and so on (Koveos, 2016).
With the help of this research, contemporary entrepreneurship practices and skills, along with competencies, need to be discussed and evaluated to understand their importance and impact on the contemporary international business scenario. The researcher here will try to explain all the aspects related to entrepreneurship and international business while linking these two concepts with proper pieces of evidence.
Research aims and objectives
This research aims to identify different terms to explain the different aspects and applicability of entrepreneurship to the international business concept. At the same time, it would also intend to evaluate its impact in the same context (Márquez and Ortiz, 2021). Along with the research aim, the research objectives are also essential to be discussed in this regard.
- To evaluate the need for entrepreneurship practices in the Global Business scenario.
- To investigate the different entrepreneurship skills and competencies appropriate for managing Global businesses.
- To discuss the benefits of having an expert entrepreneur in the international business context.
- To detect issues in the international business scenario that an inefficient entrepreneurship practice can bring.
Research question
Along with the aim, the research questions would help create a base for the research work to gather information from different scholarly sources and develop a good literature review. Thus, the research questions are;
- Why are the entrepreneurship practices necessary for the Global Business scenario?
- What are the entrepreneurship skills appropriate for managing Global Business?
- What benefits do skilled entrepreneurs serve to the international business context?
- What challenges could faulty entrepreneurs bring to the international business scenario?
Research rationale
Since the number of global businesses is continuously rising and the environment is getting competitive enough for the businesses to focus on their internal practices and entrepreneurship aspects, the intrapreneurial skills competencies and practices are essential to be evaluated and understood for better application (Kata Kevehazi, 2017). This has directed toward the requirement of a detailed discussion of entrepreneurship in the global business scenario. It also requires boosting the concept due to the contemporary problems different entrepreneurs face in expanding and maintaining competitive advantage within the international business context. One of the main problems is identified physical distance, which would cause time differences and create difficulty in managing the business practices at an international level (Cheng et al., 2021). Example here is identified in terms of the time difference between Europe and other countries where Monday to Friday and operations of them create a complexity of managing other business practices as the time is quite different and behind it in other countries. Another issue in this regard is identified in terms of resources. The finished product has been considered a big problem in being delivered to the target market due to the different time zone differences and transportation difficulties after covid-19 (Ciravegna et al. 2018). Therefore, the rationale of this research is to focus on the different aspects related to Entrepreneurship and its relation to International Business while evaluating the impact of entrepreneurship practices, skills and competencies on the international and global organisations as well.
Research structure
This portion of the research work carried the structure of the entire dissertation, as each chapter will be evaluated in terms of its deliverables and explain how these chapters are essential for the research work.
Chapter 1: this is the first chapter which is also called an introduction, and this chapter will carry all the essential related background of the topic while it will also involve a manifestation of the aim, objective problem, and direction of the research work.
Chapter 2: This is the second chapter called the literature review. This chapter contains all the related literature on the topic while critically evaluating every aspect of entrepreneurship and its relation with international business to provide a strong formation of background to the research work.
Chapter 3: This is the third chapter of the research work known as the methodology, which contains all the information related to the method used for data collection and data analysis. in this regard, the researcher has concentrated on collecting secondary data and will analyse it comparatively to physically provide the answer was the recent questions.
Chapter 4: This is the fourth chapter where the data analysis is conducted based on the data collected from secondary sources. Suppose detailed and critically evaluated data regarding the topic will be provided to align the literature review and the research objectives.
Chapter 5: This is the fifth chapter, also known as the conclusion, and contains the summary of the entire dissertation, where a link between the literature review and the data binding will be in place to ensure that the research is developed with quality and standards.
Chapter 2: Literature review
2.1 Introduction
This research work provides an introduction to entrepreneurship in international or global business. This literature review section will deliver the importance of entrepreneurship multiplies manifold when managing international businesses. Nature and extent of entrepreneurship across countries, the benefits of entrepreneurship in international business, vital traits required in entrepreneurship for global businesses, the benefits and challenges faced by them and the skills to gain competitive advantages by an entrepreneur in global business are assessed and analyzed (Almahry et al. 2018). Entrepreneurship can also be called the creation of new innovative economic activities by taking over new ventures or renewing the various economic activities of the existing firms. Entrepreneurship creates wealth and generates value at both the firm and economic levels. This assignment focuses on the definition, concept, aspects, challenges and benefits of international entrepreneurship.
2.2. Concept and aspects of entrepreneurship in international business
Entrepreneurship contributes vitally to national economies, increasing business activities and start-up rates. To gain economic development, entrepreneurship is one of the critical mechanisms as it generates innovation and increases employment. Though it depends on various factors in the countries whether it focuses on innovation-driven and oriented entrepreneurship or growth-oriented one and to what extent they positively contribute to the national development (Bosma et al. 2018). Thus, it is essential to gain in-depth, insightful knowledge of the various types of entrepreneurship that will positively contribute to the economic outcomes.
The most significant type of entrepreneurship which affects national economic development is entrepreneurship in international business. Cross-border economic activities affect the economy positively with exports, create values, generate growth, and provide access to new markets and new technology and knowledge abroad (Oriarewo et al. 2019). Governments thus, always support international businesses and entrepreneurship as it increases exports, increases national wealth and improves the competitiveness of the national economy in terms of international markets. In the past few decades, international business entrepreneurship has become vital and a much more widespread phenomenon. The considerable trade flows in the international markets, and massive foreign direct investments by multinational companies have been the prime driving forces for this fast globalization. Today, many small and new ventures are undertaking international activities, a positive feature of the world economy (Campbell et al. 2020). These small and medium firms are growing internationally faster with more expansion and substantial commitment to global markets. This ever-increasing global economy has substantial opportunities to expand sales and markets abroad, access advanced technologies, and target specific niches (Cassar and Meier, 2018). It possesses significant threats from increased foreign competition, and thus it requires sound and efficient management with the help of an entrepreneur.
Critical concepts of entrepreneurship in international business:
According to Ciravegna et al. (2018), entrepreneurship in international business refers to discovering, evaluating, enactment, and exploiting opportunities across national borders to create future goods and services.
There are no such definite definitions of entrepreneurship. However, it involves creating new economic activities. Some researchers and authors agree that they create new organizations. Ciravegna et al. (2018) defined it as pursuing opportunities. Researchers have stated the same. Mamabolo and Myres (2020) also summarized the recognition and exploitation definition of entrepreneurship, creating economic activity (Ciravegna et al., 2018).
Entrepreneurship definitions include activities of creation of ventures and also finding new economic activities of the existing firms. It involves a successful innovation from a new idea and imitating behaviours new to the firm. The specific entrepreneurial feature of risk-taking and proactiveness are all associated with creating innovations and activities.
International business is always entrepreneurial, according to recent research. As it is associated with higher risk-taking abilities- firms face much higher risks operating in international markets. Along with this, the higher innovativeness requires a high level of product innovativeness to appeal to the foreign preferences accordingly to even get an entry into the market (Cassar and Meier, 2018). Moreover, proactiveness has to be on the toes, intelligent and quick to change strategies. Last changes occur to cope with the volatile, unstable international market to create wealth and grow economically, which are essential for an entrepreneur managing international business. International entrepreneurship involves new ventures internationalization and also SME internationalization.
The Nature/aspect of International Entrepreneurship:
Entrepreneurship in international business is the process of an entrepreneur working across national boundaries and conducting business activities in various countries. It can be licensing, opening an office for sales in another country, exporting is the main, or even giving a classified advertisement in a foreign media like newspaper or through other promotion and advertisement channels (Mamabolo and Myres, 2020). The various activities related to this enormous task of satisfying the targeted customers’ demands and needs, assessing them, and deciding on matters may also occur in various countries. In managing and handling international businesses, an entrepreneur executes his/her business model in several countries together.
Entrepreneurship in international business was utilized to untapped foreign markets that were open to exploitation and utilized by new ventures reflecting a new cultural and technological environment.
Danaee Fard (2020) defined it as developing start-ups and new ventures from inception to international business. Taking their operating standards and domain as international from the initial stages of the firm’s operations. From these seven significant themes of entrepreneurship, two characteristic themes are chosen that would contribute to entrepreneurship skills and practices and would ultimately facilitate and enhance the value creation of the business.
Tolerance of risk, uncertainty and ambiguity refers to the behaviouristic characteristic of an entrepreneur of taking risks that are well calculated and measured to the ability to absorb them. Ability to minimize risks as much as possible from the business activities and share them widely with the team and collaborators. A successful entrepreneur should always possess the vital characteristic of the ability to go for unknown and unexplored business activities with the ability to tolerate unknown outcomes and unstructured works and plans (Luo et al. 2016). A successful entrepreneur always leads from the front to take new innovative actions on uncertain paths. They first walk the steps into the uncertain ways and path, leading the whole team as a role model and authentic leader, showing them how to do it and the right direction, igniting a fire and inspiring and motivating the whole team to go for it successfully. An entrepreneur should always have the ability to mitigate conflicts arising from ambiguity. He/she should be able to solve and resolve any kind of conflict and reduce stress within the team and organization. He/she should behave calmly and diligently with the ability of high tolerance. An entrepreneur should never leave conflicts and problems unresolved due to ambiguity, as it can turn into burnout or higher stress and anxiety within the organization (Merchant, 2014).
Value creation is the bedrock of business. Entrepreneurs control and manage the whole value creation process and should be involved and oriented around it. The practical process of converting available resources into products or services having perceived value is the process of value creation. It occurs when a business or an organization effectively creates perceived value that can be sold to the existing or new customer base utilizing its resources and works. In the process, businesses earn a profit, and the customer gets their need and wants to be fulfilled by the product or service being created. These resources available may be tangible physical materials or non-physical things like time. Examples of value creation can be car manufacturers producing vehicles, farmers growing crops, or banks offering loans. This essential theme of entrepreneurship translates further into a vital structural and competitive advantage for the entrepreneurial business (Metka and Jaklic, 2020). Companies with higher value creation rates grow much faster than lower ones, and they also have much-improved access right into capital markets. They create more opportunities for employees to create new jobs, and they enjoy a much greater self-funding ability. It always sets the respective company apart from other competitions, grows and secures a long-term loyal customer base and builds a robust and distinct brand name and value to the product or service. The unique offering by the company will be seen as just a standard product in the market by the target customers without creating value for the particular product or service (Narang and Kaur, 2014). Entrepreneurs engage and manage the whole process of value creation in the business. Entrepreneurs in the global market embrace value creation as the most vital aspect and basis for business growth.
Mbaka and Isiramen (2021) came up with a much broader definition of entrepreneurship in international business, including recognizing and studying established companies across borders and its detailed comparisons. They defined it as a combination of innovativeness, proactiveness, and high risk-seeking traits and behaviours that are compared across national boundaries to create value in a business organization. It takes these traits to the organizational level (Cheng et al., 2021). It takes into account and focuses not only on the characteristics and intentions of the individual entrepreneur but also on the entrepreneurial behaviours of these firms. It clearly states that the key traits of the entrepreneurs of proactiveness, innovativeness, and risk propensities can be developed at the very organizational level.
Several authors and researchers defined it clearly as entrepreneurial activity across national borders. Mbaka and Isiramen (2021) further developed the understanding in their review article. Several research studies and works have emerged, in a wide variety of areas, including born-global ventures, sales of new international ventures, cultural roles of the nations and small and medium enterprises’ internationalization (Cnbc.com, 2021). These are also applied in several geographic contexts such as Germany, Eastern Europe, Hungary, Ireland, Israel, Slovenia, Soviet Union, Northern Ireland, Ukraine and other developing economies.
In 2021, a prominent definition was developed by Mbaka and Isiramen (2021), defining it as the combination of proactiveness, innovativeness, and risk-seeking behaviour that crosses national borders intending to create value in an organization.
The importance of entrepreneurship in global business:
In this hyper-competitive and super-fast changing global economy today, the issue of global business has become much more prominent and increasingly important. Today all entrepreneurs must possess the ability and must be able to quickly move into the world of international business (Cheng et al., 2021). A successful and good entrepreneur should always possess the ability to understand the difference between a domestic business and international business activities and decide and acts according to it. An effective entrepreneur should address:
- What are the potential and possible options available for venturing into international business?
- What are the current global strategic issues that are successful?
- How domestic and international businesses are managed differently?
There are several factors involved in converting a firm into a global enterprise. All the factors influencing the firms to convert into global enterprises need to be considered when deciding to go for the global venture’s economy, political and legal environment, and the available distribution channels present in the respective countries (Ciravegna et al. 2018). Effective communication and change management are imperative to survive and operate successfully in an international environment.
2.3. Contemporary entrepreneurship practices to gain a competitive advantage in global business.
The challenging contemporary economy refers to having a better opportunity for international businesses and the entrepreneurship aspects of being successfully practised. Not an easy fact to gain a competitive advantage in the international business while different aspects and approaches work together to develop a prospect between clients and customers. Different entrepreneurship activities or practices can help international businesses gain as much as a possible competitive advantage. However, certain constraints must be identified in the report (Mookerjee and Rao, 2021). The below points can provide a clear idea of how entrepreneurship practices can enhance competitive advantage within the international business.
In the contemporary international business and entrepreneurship scenario, skills are required to identify the business positioning in comparison to the current situation. At the same time, they should not depend on prospecting the business. In other words, every business is now looking for prospects in clients or customers. However, entrepreneurship skills and practices demand that to gain a competitive advantage, international business needs to focus on positioning their products and adapt approaches that can highlight the business practices and its deliverables (Muñoz and Kimmitt, 2019). The customers and the potential consumer market can get a clear overview of the business’s deliverables and services. This can also take strategic action toward international business expansion.
Here, it is essential to highlight the entrepreneurial marketing practices so that the contribution of such entrepreneurship practices can be discussed in terms of gaining a competitive advantage (Sky.com, 2022). Entrepreneurial marketing the discipline merges to describe the marketing aspects and crossing opportunities in uncertain market circumstances. The term intrapreneurial practices in the marketing context can be identified in the form of overall activity and behaviour of entrepreneurs who include beliefs regarding the competitive behaviour of the businesses and the drivers of marketing processes that can eventually influence consumer perspective towards the business or service or product (Head, 2020). Therefore, the two distinctive disciplines are intended to merge with each other to provide better entrepreneurship Strategies and practices to the international business so that they can survive depending on the strategy to deal with the uncertain market condition.
Value creation is one of the significant aspects of entrepreneur practices in the contemporary international business scenario where the importance of customers on a long-term basis for long-term survival needs is essential for the business. The organisation’s value proposition can be enhanced either by concentrating on the value creation or by enhancing the offering set by the business to its target consumers (Grover et al., 2018). On the other hand, when value creation is seen as the primary aspect of gaining competitive advantage, this entrepreneurial practice can help international businesses understand the importance of value creation, proactiveness, resource leveraging, and so on while enhancing competitive advantages the same time.
Value creation can contribute to the development of a business positively or negatively.
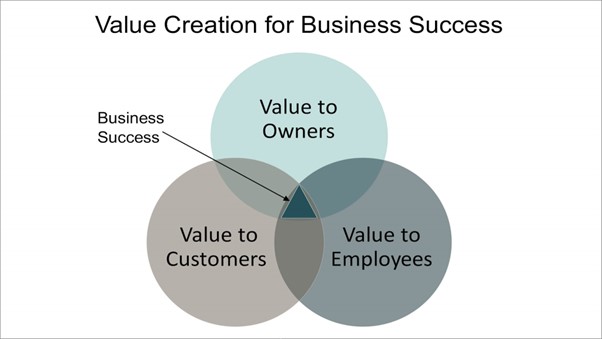
Figure: value creation using the entrepreneurship skills
Source: (Hesse et al., 2019)
Value creation is another significant aspect that refers to addressing the organisation’s need, customers and employees. In other words, value creation could help elevate the current standard of any global business by focusing on the different variety of practices, products and services.
2.4. Entrepreneurship skills required for international business
There are several skills and traits that an international entrepreneur should and must possess that are identifiable irrespective of the country of their origin. They are:
- Ability to embrace changes:
An efficient global entrepreneur will always like and embrace differences in people and situations. He/she always is on seeks to break the mould and eager for exciting things. They consistently challenge conventional corporate norms and procedures. It is a fascinating way to live by exploring different cultures and learning to do things in new ways (Hesse et al., 2019). Employees are invited, encouraged and welcome to do new things and taught to handle and embrace changes.
- Strong desire to achieve:
A good entrepreneur dealing in international business has a stronger desire to achieve and possesses good business sense and a savvy business personality. In order to succeed in this challenging condition, the entrepreneur should possess abilities to create values in different cultures and should possess the experience to face profit and loss in the business activities (Purwatmini et al., 2021). He or she should possess broad business knowledge, including foreign exchange, transfer pricing, international customs and laws in a holistic global mindset which makes up the pillars for success.
- Ability to establish a vision:
A successful international business entrepreneur must establish the vision for the organization and possess the ability to make the customers and employees understand it well. All employees should feel essential to the success and an integral part of the global organization. He/she should be very optimistic and should possess the attitude to assume everything is possible and establish short term deadlines and goals to attain the success of the vision (O’Reilly and Binns, 2019). He or she never fears to fail, possesses high intense energy levels, always works more for longer hours, and focuses on the outcomes rather than the processes.
- The ability of high tolerance:
International business entrepreneurs always view uncertainty as an opportunity and never as a threat, which allows them to develop and build mental mappings that lead to the achievement of the vision. They always possess the eagerness and passion for learning new from various sources, which broaden their minds. They undertake various initiatives which grow simultaneously without any of them completed and thus need extreme tolerance from the entrepreneur to guide them in the right direction and vision (Oriarewo et al. 2019). This makes tolerance a key factor for all entrepreneurs or companies going for international businesses.
- Possess a high level of integrity:
An excellent international business entrepreneur possesses an extremely high standard and level of company and individual integrity. The same high standards established by the entrepreneur are utilized and used in the company from the inside and outside. The employees and other business activities also require and must possess high ethical standards across all ventures.
- Giving higher importance to individuals:
Employee well-being and effectively coaching them by nurturing them is the prime focus of a good entrepreneur. A good entrepreneur works effectively in teams, inspires people and focuses on building up team spirits. He or she focuses on listening than talking and gives more excellent value to the people and individuals, whether a customer or an employee (Thornton, 2020). A good entrepreneur always focuses on building an extended sustainable enterprise in the country and abiding by their culture and law.
2.5. Benefits of an expert in entrepreneurship for global business.
An entrepreneur utilizes several resources, labour, and capital efficiently to attain the organization’s business goals. Entrepreneurs take up risks in order to make profits. But their significance is beyond just the business world and field; it helps in economic development and community enhancement by creating jobs (Mbaka and Isiramen, 2021). The benefits and importance of entrepreneurship in international business are comprehensive, and they are:
- Entrepreneurship in international business expands the market share: entrepreneurs develop a new market in international business across national boundaries introducing new products and services, and technology. Generating business growth and developments.
- It reduces production costs: practical entrepreneurship helps in the correct decisions. It utilizes the resources available in the most optimal manner, which causes a decrease in the cost of production (Economictimes.indiatimes.com, 2022).
- Help in creating a solid brand name overseas: international business entrepreneurs help build a firm brand name for the companies in the host countries and other foreign countries by effective and efficient promotion, marketing and advertisements activities and building a loyal, solid customer base.
- Boosts productivity: Entrepreneurs in global businesses boost productivity by innovating in every aspect of the business; their new ventures utilize the available resources most effectively and efficiently. They always, thus, generate new wealth and add considerable benefits to the citizens by adding to the national income (Bosma et al. 2018).
- Builds competitive advantage: entrepreneurs, in order to compete in very tough markets, uses and utilize various tools to increase the competitive advantage of the company in the international market, like the disruptive innovation theory, which gives the company a substantial competitive advantage at the cost of others (Grover et al. 2018).
- Accelerates economic growth: entrepreneurs act as wheels of economic growth of the economy and the country. They continuously innovate new products and services, generating employment and bringing accelerated economic development to the country. Large entry-level jobs and tremendous opportunities are created with the help of entrepreneurship. Unskilled workforces are converted into skilled and experienced workers promoted to more giant industries (Cnbc.com, 2021). The total increase in the country’s employment largely depends on the number of entrepreneurs coming up in the economy and their rise. They generate wealth and more national income.
- Promotes innovation: using the research and development wing rightly and effectively, an international entrepreneur succeeds in opening new income avenues through new ventures, markets, products, services and advancing their technologies. Entrepreneurs solve the unsolved problems that existing products do not deliver (Cheng et al., 2021). Thus, an entrepreneur innovates to create a product or change the existing product to deliver the missing benefits and improve the standards of people’s lives.
- Promoting social change: entrepreneurs are pioneers of bringing innovative new technological changes or systematic changes to bring changes to society. They can change, make or break any tradition or culture in society, and reduce the significant dependency on primitive methods, technologies, and systems. They can change society’s methods to bring better-improved lifestyles, improved morale, higher economic choices, and generous thinking (Hesse et al. 2019). Thus, these impact the national and international changes. There are various social innovation programs for entrepreneurs to boost social initiatives and innovation. UNICEF provides social innovation programs like the innovation accelerator for the vulnerable communities in several African countries, focusing on menstrual health and hygiene in women and girls.
- Encourages research and development: entrepreneurs always promote and encourage research and development as it stresses innovations for generating new business ideas and always thinking out of the box, meeting demands of the several countries and preferences (Bleiker et al. 2019). Entrepreneurs collect new innovative ideas, provide them proper shapes into a completely new form, and convert them into successful, feasible business endeavours. They always are on the move to discover new ideas and improve the existing ones. Their innovation in research and development has extended impact on the company, business, people and the economy.
- The combined efforts of the entrepreneurs help in the acceleration and promotion of the industry and innovation levels. They can share ideas and inspire and motivate others to plan together to start new ventures and industries (Sky.com, 2022). Thus, the importance of entrepreneurship is multi-functional.
- Improves and develops existing enterprises: international entrepreneurs develop innovative ways to expand and develop their products or services in other countries. They discover new products and services and innovate with the existing products to meet the international customers and their standards (Grover et al. 2018). Modernizing the production process, implementing new technologies from other countries due to international businesses, developing the marketing and distribution channels in other countries, and maximizing the utilization of the resources in the existing countries (Sky.com, 2022).
- International business entrepreneurship can bring many benefits and primarily impacts the country and society as a whole. It helps in the betterment of the lifestyles and livelihood of the people and innovates on social challenges and economic growth and development across country borders.
2.6. challenges of entrepreneurship that can impact global business scenarios
Entrepreneurship in international business can bring huge profits and benefits. However, it can also backfire as they face several threats from the economic environment, and the primary issue is the entrepreneur himself/herself. International business entrepreneurship is a massively complex task, sometimes resulting in ineffective managerial skills, wrong and faulty decisions, and improper use of resources, leading to the downfall of the companies in international markets (Economictimes.indiatimes.com, 2022). Uncontrollable factors like the economic factor in that market and country, political factors, and cultural and technological factors affect and make entrepreneurial decisions much more complex and challenging. The several challenges faced by the international business entrepreneurs are:
Economic challenges:
Developing a business strategy for various multi countries is dealing with different economic conditions, including currency valuations, marketing ways, distribution systems, government regulations, venture capital problems, and banking problems (Hesse et al. 2019). These complex, challenging scenarios get into each aspect of the decision making of the entrepreneurs’ international strategy and business plan formulation.
Stages of the economic development in the country reside:
An entrepreneur doing business in several countries together has to worry about the significant lack of fundamental infrastructure of roads, electricity, banking systems, communication systems, adequate educational systems, efficient legal systems, labour availability and education and skill level of the workforce dramatically affects the decisions of the entrepreneurs in international business (Mawhinney, 2020). Thus, businesses in the industrially developed countries are much easier than the developing and emerging ones. The various regional variances and relative income of the countries vary.
Balance of payment issues:
A country’s balance of payments (the difference between exports and imports) affects the direct valuation of its currency, and this affects all businesses and economic transactions within the economy directly. For example, Italy once had a severe balance of payment deficit issue which immediately resulted in a drastic and radical depreciation in their currency, the Lira. This made automobile companies export more automobiles to countries like the UK and US, even with discounts and rebates (Gbr.pepperdine.edu, 2018). They gave accessible rebates, which less affected them, and they could earn higher liras due to the decreased value of Lira. Thus, this is a significant factor and challenge that entrepreneurs face in international business.
Cultural environment challenges:
The high effect of culture is also significant in building strategies and business plans by entrepreneurs in international business. Entrepreneurs must make sure that their business plans and strategies abide and follow the local cultural norms they are operating. In some countries, displays at the time of purchases are allowed, but in some countries, they do not. Bribes and corruptions are other factors in some countries that are essential for entrepreneurs (Startuptalky.com, 2022). Dealing with these situations and finding the best course of action with the highest ethical values becomes a hardship for entrepreneurs.
Language factors: Language can also become a fundamental challenge for entrepreneurs working in various countries. They should first have and hire a translator whose target language is his native tongue.
Technological issues:
The availability and variations in technology are often surprising for entrepreneurs from developed countries to deal with. Like culture, this also varies a lot in different countries. Developed countries like the UK, US, and Germany produce uniform standardized products to meet the high level of standards in the market. But for, the developing and underdeveloped things are every opposite, and they lack behind in technological provisions (Thornton, 2020). Thus, entrepreneurs need to work and decide accordingly.
2.7 Research Gap
The research gap can be identified in terms of the critical aspects involved in the topic. At the same time, the literature has delivered an ample amount of information regarding entrepreneurship and its application in international businesses. Therefore, the gap can be identified because more in-depth ideas and information related to entrepreneurship could have been discussed. The researcher could have discussed a more in-depth analysis of the different themes related to entrepreneurship. Apart from this, the practice of entrepreneurship is another essential idea related to competitive advantages, which required more specific idea formation and analysis in the same context (Lounsbury et al., 2019). The gap is there due to the limited discussion and information regarding the role of value creation in enhancing entrepreneurship observation presented regarding the Hence; it could be stated that the literature review of research work is quite an informative, but there is more room for improvement which will make it viable for future references.
2.8 Summary
To summarize this chapter, it can be stated that the literature review has been evident in providing a critical and in-depth analysis of entrepreneurship in international business. On the other hand, this literature review has been formally discussing the concept of entrepreneurship while getting a better analysis of the facts related to the different entrepreneurship practices that can help International enhance its competitive advantage. On the other hand, it has also focused on identifying the benefits of entrepreneurship skills and competencies and the challenges of international businesses. At the same time, a separate discussion is also delivered on the manifestation of specific entrepreneurship skills that can support and help international businesses to flourish.
Chapter 3: Methodology
3.1 Introduction
This is the 3rd chapter of the dissertation, which is also known as the heart of the research work, where all the techniques and the methods related to the data collection and data analysis will be discussed. In relation to deliver a better idea about the methods utilised during the research work development, it is important to understand the type of philosophy, research approach, research design, sampling and data collection methods adopted by the researcher to in evidently answer the research questions (Alavi et al. 2018). Therefore, the following points of the research methodology will explain the research philosophy the researcher has considered, along with the different methods and approaches that have provided at most support in collecting relevant data.
3.2 Research Philosophy
In the context of involving the research philosophy, it is important to understand the research philosophy holds a significant place in a research work which contributes to developing a strong foundation for the research work to be continued and proper data, to be collected. While conducting research work, a researcher needs to understand that there are several research philosophies available which can deliver different results for the research purpose. In the context of this research work, the researcher has concentrated on adapting the interpretivism philosophy. This kind of philosophy can deliver good research for the selected topic in a subjective manner while considering the social sciences and their circumstances. Therefore, concerning this research work, the interpretivism philosophy will focus on Entrepreneurship and its subjective application. In the context of international business. Without disturbing the natural phenomenon (Blessing and Chakrabarti, 2009). Therefore, research philosophy will provide the entrepreneurs with humanistic characteristics to be explored and cater to influence over the global business scenarios.
3.3 Research approach
Research approaches are another essential element of the research work, and it will help prepare a proper background for the data, and the relevant information will also be adhered to. Concerning the research works, there are two different research approaches are identified, such as the inductive research approach and the deductive research approach. The inductive research approach refers to drawing conclusions based on the generalization and theories included in the literature review. The deductive approach refers to providing an opportunity to extract the required amount of information from the existing data sources while eliminating the irrelevant ones. Therefore, in the context of this research work, the inductive research approach is adopted to allow the author to develop a conclusion based on the theories and the literature (Hanington, 2015). The inductive approach will also help the researcher to extract information from the available resources and utilise that information to interlink the ideas. A deductive approach is required for the formulation of a hypothesis, and this particular research work has concentrated on discussing the theme-based secondary data sources. Therefore, only the inductive approach will be relevant for the project.
3.4 Research Design
The research design refers to the way of developing the research structure and adhering to the required information that would elevate the standard of the answers to the research questions. In relation to discussing the research design, three main designs can be identified such as. Exploited research design, explanatory research design and descriptive research design. Concerning this research work, the author has focused on adopting a descriptive research design as it will help in designing the detailed indulgence of the research topic and help in expanding the research problem to its core so that proper solution for the issue can be identified (Lehtonen, 2021). Along with this, the selected research design will help the researcher to incorporate more details regarding the research topic and add descriptions which will definitely address the problems within the research phenomena. At some point, the researcher also has considered the adoption of exploratory research design impact. It was denied later on, as it will only help the researcher to focus on the research problem rather than juggling with the solutions at the same time. Therefore, it is realised that the research work requires a detailed revelation of the impact of entrepreneurship and the role of entrepreneurship activities in the international business, which can only be attended by the descriptive research design.
3.5 Sampling
For any research, work sampling plays a significant role in terms of collecting the right source of data and evaluating the importance of those sources to the research work for answering the research questions. As this research work is entirely following the secondary research, therefore sampling would not be required for this particular project. In general, sampling. Mainly considered. In the context of research work to gather information from the human subjects that can provide a better overview or perspective regarding a topic. Generally, sampling often considered in a research work when the human subjects are involved and the researcher intends to extract information out of the human subjects under the primary data collection (Alavi et al. 2018). As this research has evidently manifested, the need for secondary data will involve journal articles, news articles, books, and so on. Therefore, this leads to the non-involvement of any type of sampling technique within the research work.
3.6 Data Collection
Data collection can be considered the crucial part of a researcher of development where the data collection methods and sources need to be clearly stated. In the context of this research work, the data collection process is completely based on the secondary sources where the researcher would be looking for the relevant information by going through the secondary data. Depending on the requirement of the research work, the author has decided to focus on the theme-based evaluation of data, and in order to do that, different themes of entrepreneurship in international business are investigated. After going through all the aspects, the author has focused on developing the data collection process by concentrating on two aspects related to entrepreneurship in international business, which are value creation and risk tolerance. To adhere to the requirement, the researcher has concentrated on involving different secondary sources that are evident in providing proper scenarios regarding value creation in international business and risk tolerance in the global business scenario (Sileyew, 2019). Therefore, these secondary sources will be collected based on the themes and the researcher is very much focused on adopting the secondary sources that are only providing information regarding these selected aspects of entrepreneurship.
3.7 Data Analysis Techniques
Data analysis is another important part of the research for development where the data regarding the research topic will be collected and analysed using certain techniques. In relation to this research work, the data collection has been conducted considering the secondary data sources where the author has considered several secondary sources related to the research topic and chosen those research sources by deciding on two themes. Hence, it is realised that the researcher has focused on utilising these two things such as value creation and risk tolerance in the context of international business and accumulated data from the secondary sources. Several secondary sources will be evaluated in a theme-based analysis where the two themes will be analysed and investigated regarding their relevance in the international business and impact on the entrepreneurship activities in the global organisation of the scenario (Vandenberg, 2011). Hence, this theme-based analysis refers to having better implications for answering the research questions and adhering to the requirements of the research work.
3.8 Ethical Considerations
Though ethical considerations are mainly for the primary data collection for primary research involved in areas in this regard, the ethical considerations in conducting the secondary data collection can on so be involved. In the context of considering the moral action of the research work, it is important to focus on the different aspects that can validate the secondary data collection and analysis. While doing the secondary data collection, the research needs to focus on two main aspects validity and reliability of the different aspects associated with the project. validity and reliability are crucial for ensuring the relevance and authenticity of the secondary research conducted, while it would also help in eliminating the wrong information that could result in drafting outcomes. In this regard, the researcher has the responsibility to ensure that all the ideas are collected regarding the research problem identified and are evident in answering the research questions (Stoecker and Avila, 2020). Apart from this, the authenticity of the secondary sources is also important to be identified here, as it will deliver a clear implication towards providing a better idea about the validity of the information incorporated to address the research questions at the same time. Hence, the below ethical aspects could be considered while selecting the secondary sources and considering data analysis as well.
- Secondary sources will be collected only based on the theme of the research and topic, specifically the themes are chosen.
- The authors of the secondary sources or the university need to be informed regarding the selection of the secondary sources (Hanington, 2015).
- Proper credit to the authors for using their information in their articles should be given.
3.9 Summary
To summarise the methodology section, it can be stated that the researcher has focused on secondary data analysis and, in order to support the research work, manifested the inclusion of interpretivism philosophy, which will help the researcher to analyse and subjectively study the topic. Along with this, the methodology has also manifested the use of an inductive approach and descriptive research design, which will help the author to Thor only analyse the related data and extract the relevant information. Moreover, the secondary data collection will be conducted by focusing on two themes, value creation and risk tolerance, while the researcher will concentrate on collecting secondary data sources based on these two aspects. utilising the secondary sources like journal articles, books and University libraries, the proper amount of research secondary sources will be collected and analysed thematically to extract the right information and address the research questions.
Chapter 4: Data Analysis
4.1 Brief Background of The Data Analysis
Entrepreneurship is something that refers to having a clear idea about the practices of entrepreneurship and organisational development where specific skills and competencies can be implemented to attain certain business goals. In the context of data analysis, research has focused on several secondary sources that are effective in providing different perspectives regarding entrepreneurship and its two chosen theme. Here, the researcher has concentrated on discussing the different themes of entrepreneurship, such as value creation and risk tolerance (Narang and Kaur, 2014). Resources have been selected that are evident in providing the clear implication and idea about value creation under the entrepreneurship practice and how organisations are getting impacted by those aspects in an international business environment. On the other hand, risk tolerance is also identified as the potential skills and entrepreneurship practices That have evidently manifested in the areas of international organisations in soliton risks and handling the potential risks with entrepreneurship skills. Therefore, the data analysis part will explore different aspects related to value creation, risk tolerance and entrepreneurship in international business with solid evidence.
4.2 Analysis of The Secondary Data
Yang et al. (2013) have aimed at focusing on the development of entrepreneurship spirit at the global business level and environment at the Maspion company situated in Indonesia. It stresses that long-term national scale economic development induces and creates entrepreneurship spirit development at the global environment level. It states that the entrepreneurship spirit development in the global environment is the ability of entrepreneurs to handle human resources, be constantly vigilant, prudence, long term thinking, learn from experience, continues to grow attitude, and cooperate in partnerships.
It focuses on the importance of developing an entrepreneurship spirit along with the traits and attributes developed to manage and handle business at the global standard and environment. Along with this, it stresses that economic growth induces entrepreneurship development, and it is the primary factor for entrepreneurship development. Where there is economic growth and development, entrepreneurship development and a rise in the number of entrepreneurs take place in the economy (Nishitani and Kokubu, 2011). It has given a detailed study on the barriers in the path of entrepreneurship development and has also researched the ways and efforts required to overcome them. Moreover, the fact that entrepreneurship development included in the global environment has a long-term national scale process at the economic level or sector-based involving business development. Entrepreneurship explains the spiritual development, the ability to handle various managerial aspects such as handling the human resources, thinking long term, continuing to grow, the prudence of the entrepreneur, constantly vigilant, being a quick learner from the experiences, and the ability to cooperate with others in partnerships.
On the contrary, this study is only researched based on only one company, i.e., the Maspion company Indonesia; thus, the findings from the research can never be generalised to all the entrepreneurs in the economy or sector. Using the historic constructive method as the research methodology makes it invalid for current and future entrepreneurs. The current condition has had radical changes and needs drastic changes in entrepreneurship skills and management. It mainly focuses on the past historical events of the entrepreneurship world in the global environment and concludes. It ignores the social and cultural factors which are massively responsible for affecting and influencing the entrepreneurship behaviours and activities and, thus, in the development of their spirits. Environmental factors should be the main focus on developing entrepreneurship attitudes and spirits to create a future business with products and services sustainable for the long term and are environment friendly and save the environment. It largely lacks a diversity of the research subject, and a much larger quantity of subject analysis should be taken to make the representation of the actual entrepreneurship environment to generalise the findings. Only a single study site has been taken in the research making it inaccurate to account for entrepreneurship development for generalisation. Much larger study sites must be taken to make the data and information accurate. It ignores various technical, managerial and vital entrepreneurial skills such as innovation and focuses on change orientation, planning, motivating, decision-making, designing, research development and environmental observations.
Stocker and Abib, (2019) tried to explain global entrepreneurship with case studies of entrepreneurial firms operating around the world. It focuses on the gap that entrepreneurship is taught everywhere globally. However, these often miss out on the proper references and real-life case studies to make studies have deep insight and analysis into the subject, especially for international students. It primarily focuses on assessing the entrepreneurship activities and developments in the particular environment of a specific operating firm in a particular country around the world.
This facilitates students with in-depth insights into global entrepreneurship by bringing together various expert entrepreneurship scholars to provide a collection of global case studies regarding the various entrepreneurship firms operating around the world. This study is beneficial and unique as it covers a wide variety of issues and topics related to global entrepreneurship, such as the corporate aspect of entrepreneurship, indigenous entrepreneurship, and the social aspect of global entrepreneurship. It contains selective, credible and reliable real-life case studies of global entrepreneurship from selected operating firms. It is credible and reliable as it is done by expert scholars of the world in global entrepreneurship. Entrepreneurship instructors worldwide can use this for classroom discussions, assessments or analysis.
It is an ideal supplement for many texts and introductory classes and texts to make students, researchers, and others better understand entrepreneurship at the global level. It can be a stand-alone reference and case study collection on global entrepreneurship for the help of students, researchers and educators. This study aims at a better in-depth understanding of the subject of global entrepreneurship and a wide variety of other relevant aspects of it (Hesse et al. 2019). This study is highly beneficial to students worldwide, especially international students.
It focuses on case studies from operating entrepreneurship firms worldwide with no study into the entrepreneurship definitions, roles, characteristics, traits, or any other vital aspect. It is merely a collection of case studies on global entrepreneurship in the operating firms in various countries. It does not narrow down any particular sector or industry (Chaudhry et al. 2019). Thus, not suitable for particular industry students or researchers to follow and use. Global entrepreneurship is a vast subject. It does not mention anything about its analysis and assessment of the firms’ entrepreneurship activities, but it just mentions what happened and what is the future.
This research study of Dodo et al. (2017) aims at bridging the gap of literature by analysing and studying the magnitude of the impact of value creation networking, growth orientation, opportunity orientation, total customer focus, informal market analysis and closeness to the market dimensions have on the entrepreneurial marketing behaviour (EM) of the start-ups and scale-up companies. This study’s main primary goal and objective are to identify whether there is any difference between entrepreneurship marketing behaviours in a start-up and a scale-up company. This research involved a massive 406 start-up and scale-up business owners across Indonesia; interviewed them for a long time and supplied questionnaires to collect vital data and information regarding their behaviours and reactions to the changes in various factors. The study took companies operating for less than six years as start-ups and companies operating for more than six years as scale-up companies. Snowball sampling was made to select the companies from the whole of Indonesia.
It focuses on value creation as one of the most dominant and essential concepts of Entrepreneurship marketing behaviour (EM). It took a considerable number of companies for sampling, 406 start-ups and scale-up companies across Indonesia, as their sampling and interviews were taken regarding the changes in the entrepreneurship marketing behaviours, which makes the results credible enough. It focuses on the significantly less researched and studied topic of the difference between entrepreneurship marketing behaviours in start-ups and scale-up companies and bridges the gap in the literature. It dives deep into the entrepreneurship marketing behaviour (EM) definitions and aspects and specific characteristics related to it.It also stresses that value creation is one of the most dominant factors and dimensions in both the start-ups and scale-up companies. It clearly states the differences in the approaches made in start-up and scale-up companies regarding their marketing activities. It also states the ways and differences in approaches by start-up companies and scale-up companies regarding seeking opportunities and tapping the potential opportunities for business growth. It also states that start-up companies are much better equipped to handle, communicate, and build customer relationships than a scale-up company. It mentions that start-up companies are much more flexible, opportunistic, innovative and quick to make changes and quick decision-makers than scale-up companies. Thus, their growth rate is always higher than the scale-ups.
It uses two hypotheses in the research study, value creation networking as the most dominant factor and dimension in a scale-up and start-up company. Secondly, start-up companies require higher entrepreneurial marketing activities and behaviours than scale-up companies. Thus, the result and findings from this research study are according to these two hypotheses. The questionnaires and interviews taken take into account the two hypotheses and not in general. The results obtained are regarding the definite particular set of dominant factors and dimensional changes and their possible changes. The dominating driving factors played a vital role in the research results. It is not a real-life scenario case study or fact, and it is just the result of the interviews and answers from the questionnaires given by the business owners. These can be flawed depending on the owner’s condition at that time of the interview or answering the questionnaire.
This research study by Mamabolo and Myres (2020) is a single case study of an evolving business model that accounts for social rewards/risks in a small lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm in the UK. It aims to investigate the need for an evolving business model that actually accounts for the social as well as for the business-related risk and rewards considerations. Its main objective is to research and investigate an evolving business model which would be beneficial largely for both the business and social related rewards and risks as businesses should also have social responsibilities and should bring and development and betterment of society as well (Mamabolo and Myres, 2020). This study contains a research question that can an evolving business model that accounts for social risk and rewards assist the enduring nature of a small, lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm.
This investigation follows the interpretive sensemaking approach of Welch and others, emphasising the contextualisation strongly, and weak causal explanations from a single case study are further strengthened. It aims at providing an exemplar of the research question addressed and not generalising the results and outcomes. The use of exemplar gives greater insights to the students and future researchers as it is a story from which researchers can compare their experiences and gain greater rich theoretical insights. It bridges the gap between the theoretical and practical aspects of a better understanding of the behaviours and attitudes of the owner-managers in the view of attaining different objectives and employing different business models. It focuses on the entrepreneurship skills sets or owner-manager set of skills to manage the business effectively and efficiently (Grover et al. 2018). It focuses on the effective implementation of the rightly selected strategies and proper goal setting by the owner-manager, and having correct behavioural perspectives. It stresses the fact that just learning will never be enough. Effective implementation of the learnings can help build resilience among the owners and managers. It mentions the importance of setting proper objectives and implementing risk/reward decision-making to meet them. Need to assess, plan and manage resilience with social, economic and environmental factors into account. It stresses that the proper selection of an effective and suitable business model is equally important.
This research on a single case study and was done on one sample size, which makes it very hard to establish a generalisation even though several data collection methods have been used. Generalisation outside the boundaries of the research cannot be performed. The use of qualitative data and the interpretations of the qualitative data differs depending on various factors. It used manual coding of the data analysis as it can be flawed and create doubts about the trustworthiness of the data. This research study deals with the owner and manager from the LGBT community of a small lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm that is actually operating in a rural community which is very conservative, and thus, situations and conditions will vary and change drastically in a more liberal urban setting (Chaudhry et al. 2019). The positive effects of social relationships and bonds are not well mentioned and highlighted in this study. It only studies a single case of owner-managers from the LGBT community, and non-LGBT community owner-managers are ignored. No expansion of the research in line with this case study of owner-managers not belonging to the LGBT community also needed to be performed. The resource-based views, contingency-based views and network-based views are not taken into consideration.
This research study by Oriarewo et al. (2019) represents case study based on an empirical study about the implementation of the strategies of value creation in a manufacturing firm in China. This study focuses on implementing the value creation strategies in the Chinese steel manufacturing firm, the first company in the Chinese steel industry, and it illustrates how the firm creates value from the managerial perspective. It discusses and analyses the rich account of the process of value creation. The theoretical and managerial aspects highlight the value creation and the challenges faced by the managers.
It gives a detailed study of the firm and its strategies implemented in the production and business process with its historical past. It provides an in-depth analysis of why the steel manufacturing firm ZISCo was in dire need of a value creation strategy to be implemented.
There is a lack of any definite boundaries within the phenomenon and the context, and they are not evident. Thus, the case study approach is selected as their research methodology. It gives a detailed study and analysis of the failure and poor condition of the firm before applying value creation functions. It also provides an in-depth study of the past business model and strategy used, i.e., the use of differentiation strategy used in the production and business process, and mentions several factors and reasons for selecting this strategy at that time (Burgel and Murray, 2000).
It mentions the compelling reasons why the differentiation business strategy failed after implementation in the steel manufacturing firm with a detailed analysis. It gives importance to reviewing processes and strategies before a new business model or strategy needs to be implemented. It provides clear steps for implementing the process of value creation with an in-depth analysis of each step-in detail.
It does not mention and recommends any solutions to the various challenges faced by the chines steel manufacturing firm ZISCo in implementing the value creation strategy in their production and business process. The case study approach used in the research methodology has various limitations to the study’s analysis, results, and findings. It does not facilitate resolving the problems of the firm. Just merely mentions the problems and what had happened during the incidents, and what the firm implemented in reaction to trying to solve the problem. It does not recommend any further steps to make the implementation of the value creation strategy more effective and beneficial for the firm, decreasing the negative implications of the process (Purwatmini et al. 2021). This is just a case study of a particular steel manufacturing firm in China, and these steps and incidents may be feasible and happening in other parts of the world, and thus, any research findings from this study will not be able to generalise for the global companies around the world. It lacks any kind of theory building or theoretical data improvements. As a single case study, it lacks generalisations to be established.
This research study by Grover et al. (2018) is a single case study of an evolving business model that accounts for social rewards/risks in a small lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm in the UK? It aims to investigate the need for an evolving business model that accounts for the social and business-related risk and rewards considerations. Its main objective is to research and investigate an evolving business model that would be mainly beneficial for both the business and social related rewards and risks as businesses should also have social responsibilities and should bring and development and betterment of society. This study’s research question is whether an evolving business model that accounts for social risk and rewards can assist the enduring nature of a minor, lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm.
This investigation follows the interpretive sensemaking approach of Welch and others, emphasising the contextualisation strongly, and weak causal explanations from a single case study are further strengthened. It aims to provide an exemplar of the research question addressed and not generalise the results and outcomes. The use of exemplar gives more significant insights to the students and future researchers. It is a story from which researchers can compare their experiences and gain rich theoretical insights. It bridges the gap between the theoretical and practical aspects of a better understanding of the behaviours and attitudes of the owner-managers to attain different objectives and employ different business models. It focuses on the entrepreneurship skills sets or owner-manager set of skills to manage the business effectively and efficiently. It focuses on effectively implementing the rightly selected strategies and proper goal setting by the owner-manager and having correct behavioural perspectives. It stresses the fact that just learning will never be enough. Effective implementation of the learnings can help build resilience among the owners and managers. It mentions the importance of setting proper objectives and implementing risk/reward decision-making to meet them. Need to assess, plan and manage resilience with social, economic and environmental factors. It stresses that selecting an effective and suitable business model is equally important.
This research was done on a single case study was done on one sample size, making it very hard to establish a generalisation even though several data collection methods have been used. Generalisation outside the boundaries of the research cannot be performed. The use of qualitative data and the interpretations of the qualitative data differs depending on various factors. It used manual coding of the data analysis as it can be flawed and create doubts about the trustworthiness of the data. This research study deals with the owner and manager from the LGBT community of a small lifestyle-oriented family-owned firm that is operating in a rural community which is very conservative (Stocker et al. 2021). Thus, situations and conditions will vary and change drastically in a more liberal urban setting. The positive effects of social relationships and bonds are not well mentioned and highlighted in this study. It only studies a single case of owner-managers from the LGBT community, and non-LGBT community owner-managers are ignored. No expansion of the research in line with this case study of owner-managers not belonging to the LGBT community also needed to be performed. The resource-based views, contingency-based views and network-based views are not considered.
This research study by Syaifuddin (2021) aims at bridging the gap of literature by analysing and studying the magnitude of the impact of value creation networking, growth orientation, opportunity orientation, total customer focus, informal market analysis and closeness to the market dimensions have on the entrepreneurial marketing behaviour (EM) of the start-ups and scale-up companies. This study’s main primary goal and objective are to identify whether there is any difference between entrepreneurship marketing behaviours in a start-up and a scale-up company. This research involved a huge 406 start-up and scale-up business owners across Indonesia who interviewed them for a long time and supplied questionnaires to collect vital data and information regarding their behaviours and reactions to the changes in various factors (Lounsbury et al. 2019). The study took companies operating for less than six years as start-ups and companies operating for more than six years as scale-up companies. Snowball sampling was made to select the companies from the whole of Indonesia. It focuses on value creation as one of the most dominant and important concepts of Entrepreneurship marketing behaviour (EM). It took a huge number of companies for sampling, 406 start-ups and scale-up companies across Indonesia, as their sampling and interviews were taken regarding the changes in the entrepreneurship marketing behaviours, which makes the results credible enough. It focuses on the very less researched and studied topic of the difference between entrepreneurship marketing behaviours in start-ups and scale-up companies and bridges the gap in the literature. It dives deep into the entrepreneurship marketing behaviour (EM) definitions and aspects and specific characteristics related to it. It also stresses that value creation is one of the most dominant factors and dimensions in both the start-ups and scale-up companies. It clearly states the differences in the approaches made in start-up and scale-up companies regarding their marketing activities (Stocker and Abib, 2019). It also states the ways and differences in approaches by start-up companies and scale-up companies regarding seeking opportunities and tapping the potential opportunities for business growth. It also states that start-up companies are much better equipped to handle, communicate, and build customer relationships than a scale-up company. It mentions that start-up companies are much more flexible, opportunistic, innovative and quick to make changes and quick decision-makers than scale-up companies. Thus, their growth rate is always higher than the scale-ups.
It uses two hypotheses in the research study, value creation networking as the most dominant factor and dimension in a scale-up and start-up company. Secondly, start-up companies require higher entrepreneurial marketing activities and behaviours than scale-up companies. Thus, the result and findings from this research study are according to these two hypotheses. The questionnaires and interviews taken take into account the two hypotheses and not in general. The results obtained are regarding the definite particular set of dominant factors and dimensional changes and their probable changes. The dominating driving factors played a vital role in the research results. It is not a real-life scenario case study or fact, and it is just the result of the interviews and answers from the questionnaires given by the business owners.
4.3 Discussion and Findings
In this study, we find how and why the fast and rapid internationalizing firms and born global firms can link their business models with the entire process of their business operations and implement them successfully and effectively. It mainly develops a theoretical framework for implementing the value creation business model from the various sources for the born global companies and international new ventures. It finds out the relation between the internationalization of the companies and their value creation business models implemented by the born global companies (Forbes.com, 2022). It also delivered that the new tech-based firm’s internationalization is a multidimensional, knowledge-based and relational augmentative process.
The entrepreneurship, innovation and internationalization of these new tech-based companies should be taken as a holistic approach.
- They have defined the value creation business model concerning the three vital managerial decisions and activities.
- The selection of the activities.
- The location of the activities.
- Internal organization and designing the value network.
The study finds that the born global companies usually pursue global niche markets by offering one unique product. The choice of activities determines the company’s competitive environment, and it can strategically plan and place itself safe from confronting the larger MNCs.
This study finds evidence that suggests that the structural features and characteristics of new global companies, like global competencies, shorter life-cycle and dynamic nature, are the fundamental reasons for fostering and facilitating rapid internationalization (Cassar and Meier, 2018). Their low cost of transportation, adaptation, and information also fosters these born global companies to rapid and fast internationalization.
It finds out that the born global companies always focus on the product or service development and outsourcing processes, which are not vital and are less critical. Global companies balance the insourcing and outsourcing relations and activities efficiently and effectively, which is vital. They always focus on strategic alliances and partnerships, which typically assure easy access to information, complementary resources and capabilities, allowing them to compete globally.
This study found that for the location of the activities (locus), born global companies used to make or buy decisions for the direction and scope of internationalization. The offered products or services determine the direction of international expansion. The level of global industrial integration determines the scope of foreign operations. They choose leading markets according to the infrastructure needed for the sales operations and the size of local niche markets (Bleiker et al. 2019).
It gives a detailed idea of the strategies and business models implemented in the Chinese steel manufacturing firm, ZISCo. It finds out why the differentiation strategy and business model failed in the firm and why it required the value creation business model so essentially to be implemented into their process. It finds the importance of value creation as one of the most dominant and essential concepts of Entrepreneurship marketing behaviour (EM). It finds the difference in the entrepreneurship marketing behaviour in start-up and scale-up companies regarding their marketing activities. It finds out the different approaches and ways used by start-up and scale-up companies to tap the potential opportunities. It finds out the theoretical and practical gap in the behaviours and attitudes of the manager-owners regarding attaining different objectives and implementing the different business models. It finds that effective implementation of the learnings can build resilience, risk tolerance, and adaptability. It finds out the importance of a set of skills of the owner-managers to manage the business effectively and efficiently (Stocker and Abib, 2019). The selection and proper implementation of an effective business plan are vital.
It finds out the various aspects of risk tolerance and risk management of seven born global Brazilian companies. It finds out how and how the born global companies manage the risks. The findings from this study highlight the ways and how risks are perceived in the born global firms by the managers in internationalization. It also finds that these companies use different classifications of risks into monetary, commercial, intercultural and country risks. They have identified that these enterprises use different ways and actions to mitigate risks, such as building scenarios, planning and market research (Márquez and Ortiz, 2021). It finds vital factors by which risk can be minimized, such as the international background of the entrepreneurs or the managers and the use of value networks. It finds and proposes an integrated risk management model for internationalizing born global companies. The integration model of risk management presented in the study identifies and evaluates three essential items in the internationalization process of the studied companies: the use of networks, the choice of internationalization strategies, and the speed of internationalization. It finds out the risk factors of the born global enterprises that vastly differ from traditional small businesses. The assessment and risk analysis are done on the internal and external environment of the born global (Márquez and Ortiz, 2021). It finds that the international background of the entrepreneurs and managers plays a vital role in minimizing risks by having relationships in several social networks, and thus much fewer risks are perceived.
Chapter 5: Conclusion
5.1 Concluding Summary
In the conclusion, the summaries of the entire dissertation can be delivered where the author has decided to manifest a clear implication of entrepreneurship and its different aspect in the context of global entrepreneurship. The entrepreneurship is a concept that refers to the practices that would help the multinational organisations to attain competitive advantages and organisational value at the same time. The research work has concentrated on several aspects of entrepreneurship by focusing on the two different areas such as value creation and risk tolerance in international business scenario. Value creation refers to the activities that an organization needs to consider while implementing entrepreneurship skills and competencies. Value creation is something that refers to an organisation’s ability to address the requirement of the organization, its employees and its customers. The conclusion is the summarized form of the entire dissertation, where the brief idea about the discussion in the above chapters can be delivered. Entrepreneurship in the international business here is presented as a definite form of business practice that multinational organizations need to consider. While it will also provide a clear idea of how entrepreneurship skills can elevate and organizational performance and future sustainability. Therefore, this chapter will be evaluating the connection between the literature review and the findings based on the research objectives, and a link will be placed to understand whether the research works. Evidently addresses all the research objectives and its questions. With enough evidence and information, the aspects will be discussed in the following manner.
5.2 Linking with The Objectives
1) To evaluate the need for entrepreneurship practices in the Global Business scenario.
In order to understand the requirement of entrepreneurship practices in the global business scenario, it is important to highlight that the entrepreneurs in the global business help in boosting the economic growth of the organization. By concentrating on innovative technologies. In other words, entrepreneurship practices can refer to involve products and services delivered to the consumer market with more effort incorporated. The increased competition has compelled multinational organizations to think about more efficient and skilful entrepreneurship practices so that the challenges can be dealt with in a competitive manner. Here the literature review has manifested wide and vast information regarding the entrepreneurship skills and competencies that entrepreneurs in the contemporary competitive environment require, and those skills can help organizations in the global business scenario to attain their objectives. The literature review has also delivered a clear indication of the requirement of entrepreneurship practices in the global business scenario, where different organizations have been exhibiting their requirement regarding the entrepreneurial skills and its impact over the economic growth. Hence it can be stated that the findings have also provided a vast information over the different organization implementing the different themes of entrepreneurship, that is, value creation and risk tolerance. Therefore, the link between the literature review and the research objectives can be found in a clear manner as the findings have been justified and supported by the facts with strong evidence.
2) To investigate the different entrepreneurship skills and competencies appropriate for managing Global businesses.
The literature review has delivered a wide range of information regarding an efficient entrepreneur’s skills to understand the required intrapreneurial skills and competencies. The literature review has discussed the range of skills that an entrepreneur needs to possess in an international business scenario. Those skills and competencies are evident in creating better prospects for the business and management process. The literature review has discussed a wide range of skills and competencies involved in entrepreneurship practices, such as the ability to establish a vision, ability to manifest high tolerance, High level of integrity, Higher individual importance and so on. these aspects of entrepreneurship skills are evidently manifested in this regard while the findings also adhere to the express that how the modern entrepreneurs are able to attend organisational needs by manifesting organisational skills. Therefore, it can be stated that the literature review is directly linked with the objective of the research work as the findings and worked as strong evidence in due course.
- To discuss the benefits of having an expert entrepreneur in the international business context.
The objective of the research work has manifested the intention to investigate the importance of having an expert entrepreneur in the international business scenario. It is observed that the literature review has provided a detailed evaluation of the same topic. In the literature review chapter, the researcher has intended to incorporate as much as possible information on the importance of entrepreneurship and having an expert entrepreneur on board. One of the importance of having an expert entrepreneur in the international business is identified with the fact that they help in accelerating economic growth. On the other hand, expert entrepreneurs can promote innovation within the organisation when the economic standard requires the company to be innovative and creative in the product delivery process. The literature review has also many tested that Entrepreneurship and an expert skill holder in intrapreneur practices can simultaneously promote social changes and organisational culture development. This has clearly shown that entrepreneur loss can deliver changes within the organisational practices that will adhere to the social changes or social standard elevation at the same time. Therefore, it can be stated that the research work has evidently addressed the research objective with the help of the literature review. It has added a clear indication of having a strong finding simultaneously.
- To detect issues in the international business scenario that an inefficient entrepreneurship practice can bring.
In order to successfully carry out the international business, entrepreneurs need to have certain skills and competencies, which were discussed in the previous section of the literature. Along with the benefits, entrepreneurship and its issues could create huge incompetence in the course of international business. The literature review has significantly manifested the impact of an incompetent entrepreneur in the international business scenario, which could create evident issues like financing hurdles to the business organisations and inadequate management for the employees of the organisations. Apart from this, an incompetent entrepreneur could create a significant amount of ineffective business planning that will eventually influence the organisation’s financial development. On the other hand, the lack of expertise in the entrepreneur was can create a significant amount of marketing mishaps, which eventually contributes to the rising complexity of the product delivery service delivery and failure of the international business. The literature review has evidently highlighted the challenges related to inefficient entrepreneurship practices or the lack of proper application of entrepreneurship skills in the international business, which manifested its future impact at the same time. Moreover, it can be stated that the literature review and the findings have been evident in addressing all the aspects of the research and provided a clear link between the research objective and the discussed literature at the same time.
Based on the above discussion of the linking between the literature review and the research objective, it can be stated that the researcher has focused on different aspects related to entrepreneurship in the international business scenario. Tab discussion has manifested a clear indication of a clear link between the literature review and the research objective, as the researcher has focused on specific information that can adhere to the research objective and its requirement to fulfil the research questions with proper answers at the same time. Therefore, the findings have played a significant role in this regard at the same time as they have a backup the statements are the objectives with proper evidence, while different case scenarios have been delivered to manifest how Entrepreneurship and its different things like value creation and risk tolerance have been contributing the idea of entrepreneurship and its importance in the international business scenario. Moreover, it can adhere to the fact that the research work and the main areas like literature review and the discussion of the data collected from different sources have evidently adhered to the requirement of addressing the research questions and justified the research topic for understanding the importance of entrepreneurship in the international business focusing on two different themes that the operation and risk tolerance of on multinational organisations.
5.3 Recommendation
Based on the above valuation of entrepreneurship in the international business scenario, the dissertation has delivered an ample amount of information, but there are rooms for improvement that can be delivered in the following manner in the form of recommendation. The recommendation would adhere to the idea of mitigating the entrepreneurship challenges and also would deliver a clear form of solutions for the multinational organisations towards growth and sustainability with the right practices of entrepreneurship. Therefore, the following suggestions can be considered to deliver a clear implication of effective and rightful entrepreneurship in international business.
- Contemporary entrepreneurs need to conduct in-depth research regarding the scenario the situation before making any informed decisions. In other words, an effective and efficient entrepreneur would be concentrating on making decisions backed by evidence or solid data that can eventually help in creating a better platform for future strategy implementation in international business.
- Important aspects that the entrepreneur in international business needs to focus on are developing the right structure of the decision-making and practising entrepreneurship from the very beginning. The structure of the business or planning of implementing entrepreneurship practices can manifest a different area of opening and delivering a clear decision for the company at the same time.
- Along with this, the organisations in the Global Business scenario need to consider entrepreneurship practice when the entrepreneur needs to encourage its employees to deliver their inside regarding certain decisions or provide them with the opportunity to assert their idea for the business practices to monitor capacity.
- An effective entrepreneur needs to concentrate on providing work experience schemes and, together with the internship, an apprenticeship to the employees to provide better training programs and strengthen their skills and competencies.
- The value creation strategies need to be evaluated for certain multinational organisations where the value creation should be developed for all the stakeholders, including the company employees and the customers, at the same time.
- International Business entrepreneurship is required to avoid 50-50 partnerships where businesses can get huge amounts of challenges and generally the start-up that is planning to invade the international market.
Therefore, the above statements relating to the recommendations could be effective in terms of helping the budding entrepreneurs to understand the importance of entrepreneurial skills in the international business scenario.
5.4 Limitations of The Research
Despite having a wide array of Information and the ability to address the research questions and objectives, the researcher has encountered certain limitations while conducting the research work. in the course of developing the visitation, three main limitations can be identified to evaluate its sources and reason. Three main hurdles are financial limitations, resource limitations and timing constraints. A student conducts the research work. Therefore, it is quite evident that the financial resources would be Limited and this created certain challenges for the discharge to be completed with the help of any type of investment. Another limitation is identified in terms of resource limitation, which refers to the fact that the students or the researchers have encountered the issues of limited resources for the literature review and for the data analysis part. In this regard, it is important to mention that the library of the University has helped with the required resources, despite the student having difficulty in collecting relevant information and a relevant number of sources for literature and secondary data. Apart from this, another significant constraint is the time which is denoted in terms of deadline. As the researcher had to submit the research work within a specific time or deadline, therefore, the quality of the research work might get compromised to some extent. Therefore, despite having limitations, the author has been able to create a quality and standardized piece of research which can be considered as a reference for future researchers at the same time.
References
Agostino, M., Giunta, A., Nugent, J., Scalera, D. and Trivieri, F., 2014. The importance of being a capable supplier: Italian industrial firms in global value chains. International Small Business Journal: Researching Entrepreneurship, 33(7), pp.708-730.
Alavi, M., Archibald, M., McMaster, R., Lopez, V. and Cleary, M., 2018. Aligning theory and methodology in mixed methods research: Before Design Theoretical Placement. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 21(5), pp.527-540.
Almahry, F.F., Sarea, A.M. and Hamdan, A.M., 2018. A review paper on entrepreneurship education and entrepreneurs’ skills. Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 21(2S), pp.1-7.
Arshed, N., Rauf, R. and Bukhari, S., 2021. Empirical Contribution of Human Capital in Entrepreneurship. Global Business Review, p.097215092097670.
Augustyniak, D., 2017. Sources of Value Creation in Born Global Companies. International Journal of Management and Economics, 53(2), pp.7-22.
Bleiker, J., Morgan-Trimmer, S., Knapp, K. and Hopkins, S., 2019. Navigating the maze: Qualitative research methodologies and their philosophical foundations. Radiography, 25, pp.S4-S8.
Blessing, L. and Chakrabarti, A., 2009. DRM, a design research methodology. Dordrecht: Springer.
Bosma, N., Sanders, M. and Stam, E., 2018. Institutions, entrepreneurship, and economic growth in Europe. Small Business Economics, 51(2), pp.483-499.
Burgel, O. and Murray, G., 2000. The International Market Entry Choices of Start-Up Companies in High-Technology Industries. Journal of International Marketing, 8(2), pp.33-62.
Campbell, S., Greenwood, M., Prior, S., Shearer, T., Walkem, K., Young, S., Bywaters, D. and Walker, K., 2020. Purposive sampling: complex or simple? Research case examples. Journal of Research in Nursing, 25(8), pp.652-661.
Cassar, L. and Meier, S., 2018. Nonmonetary incentives and the implications of work as a source of meaning. Journal of Economic Perspectives, 32(3), pp.215-38.
Chandra, V. and Harindran, A., 2017. Research Methodology. [S.l.]: Pearson Education India.
Chaudhry, S., Crick,, J. and Crick, D., 2019. Items in Figshare are protected by copyright, with all rights reserved, unless otherwise indicated. Risks/rewards and an evolving business model: a case study of a small lifestyle business in the UK tourism sector. Loughborough University, [online] Available at: <https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/QMR-01-2017-0001/full/html> [Accessed 11 May 2022].
Cheng, C., Lay, K.L., Hsu, Y.F. and Tsai, Y.M., 2021. Can Likert scales predict choices? Testing the congruence between using Likert scale and comparative judgment on measuring attribution. Methods in Psychology, 5, p.100081.
Ciravegna, L., Kuivalainen, O., Kundu, S.K. and Lopez, L.E., 2018. The antecedents of early internationalization: A configurational perspective. International Business Review, 27(6), pp.1200-1212.
Cnbc.com, 2021, How Amazon managed the coronavirus crisis and came out stronger, viewed on 26/03/2022 <https://www.cnbc.com/2020/09/29/how-amazon-managed-the-coronavirus-crisis-and-came-out-stronger.html>
Crick, D., Chaudhry, S. and Crick, J., 2018. Risks/rewards and an evolving business model. Qualitative Market Research: An International Journal, 21(2), pp.143-165.
Danaee Fard, H., 2020. Inductive approach to building theory: Grounded theory strategy. Commercial Strategies, 3(1), pp.57-70.
Dodo, F., Potluri, R. and Gazara, S., 2017. Sustainable Entrepreneurship among Rural Women in Nigeria: An Assessment of Benefits. Journal of Industrial Distribution & Business, 8(3), pp.5-9.
Economictimes.indiatimes.com, 2022, Coronavirus Crisis: British Airways faces strike threat over job cuts, viewed on 29/03/2022 <https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/international/business/coronavirus-crisis-british-airways-faces-strike-threat-over-job-cuts/articleshow/77216600.cms?from=mdr>
Forbes.com, 2022, A Look Back At Why Blockbuster Really Failed And Why It Didn’t Have To, viewed on 26/03/2022 <https://www.forbes.com/sites/gregsatell/2014/09/05/a-look-back-at-why-blockbuster-really-failed-and-why-it-didnt-have-to/?sh=42eebc5c1d64>
Gbr.pepperdine.edu, 2018, To Tell or Not to Tell?, viewed on 25/03/2022 <https://gbr.pepperdine.edu/2010/08/to-tell-or-not-to-tell/>
Goddard, W. and Melville, S., 2011. Research methodology. Kenwyn, South Africa: Juta & Co.
Grover, V., Chiang, R.H., Liang, T.P. and Zhang, D., 2018. Creating strategic business value from big data analytics: A research framework. Journal of Management Information Systems, 35(2), pp.388-423.
Groysberg, B., Lee, J., Price, J. and Cheng, J., 2018. The leader’s guide to corporate culture. Harvard business review, 96(1), pp.44-52.
Hanington, B., 2015. Making Methods Work: 10 Rules of Thumb for Design Research. Archives of Design Research, 113(1), p.41.
Head, G., 2020. Ethics in educational research: Review boards, ethical issues and researcher development. European Educational Research Journal, 19(1), pp.72-83.
Hesse, A., Glenna, L., Hinrichs, C., Chiles, R. and Sachs, C., 2019. Qualitative research ethics in the big data era. American Behavioral Scientist, 63(5), pp.560-583.
Kata Kevehazi, 2017. Importance of Female Entrepreneurship. China-USA Business Review, 16(7).
Koveos, P., 2016. Global Importance Of Entrepreneurship. Journal of Developmental Entrepreneurship, 21(01), p.1601001.
Lehtonen, D., 2021. Constructing a design framework and design methodology from educational design research on real-world educational technology development. EDeR. Educational Design Research, 5(2).
Lounsbury, M., Cornelissen, J., Granqvist, N. and Grodal, S., 2019. Culture, innovation and entrepreneurship. Innovation, 21(1), pp.1-12.
Luo, Xing-Wu, 강태원 and Liu, Ying, 2016. Exploring Business Model Evolution Mechanism from the Perspective of Value Creation: A Case Study of Chinese Circulation Firm. Journal of Distribution and Management Research, 19(3), pp.61-72.
Mamabolo, A. and Myres, K., 2020. A systematic literature review of skills required in the different phases of the entrepreneurial process. Small Enterprise Research, 27(1), pp.39-63.
Márquez, F. and Ortiz, G., 2021. Disruptive Thinking and Entrepreneurship: Fictions and Disenchantments. Global Business Review, p.097215092098864.
Mawhinney, T., 2020. User preferences related to virtual reference services in an academic library. The Journal of Academic Librarianship, 46(1), p.102094.
Mbaka, N. And Isiramen, O.M., 2021. The Changing Role Of An Exploratory Research In Modern Organisation. GPH-International Journal of Business Management (IJBM), 4(12), pp.27-36.
Merchant, H., 2014. Configurations of Governance Structure, Generic Strategy, and Firm Size: Opening the Black Box of Value Creation In International Joint Ventures. Global Strategy Journal, 4(4), pp.292-309.
Metka, S. and Jaklic, A., 2020. Sources of Value Creation in Service Global Value Chains. www.amfiteatrueconomic.ro, 22(55), p.846.
Mookerjee, J. and Rao, O.R.S., 2021. A Review of the Impact of Disruptive Innovations on Markets and Business Performance of Players. International Journal of Grid and Distributed Computing, 14(1), pp.605-630.
Muñoz, P. and Kimmitt, J., 2019. Social mission as competitive advantage: A configurational analysis of the strategic conditions of social entrepreneurship. Journal of Business Research, 101, pp.854-861.
Narang, S. and Kaur, M., 2014. Impact of Firm-specific Attributes on Shareholder Value Creation of Indian Companies: An Empirical Analysis. Global Business Review, 15(4), pp.847-866.
Nishitani, K. and Kokubu, K., 2011. Why Does the Reduction of Greenhouse Gas Emissions Enhance Firm Value? The Case of Japanese Manufacturing Firms. Business Strategy and the Environment, 21(8), pp.517-529.
O’Reilly, C. and Binns, A.J., 2019. The three stages of disruptive innovation: Idea generation, incubation, and scaling. California Management Review, 61(3), pp.49-71.
Oriarewo, G.O., Ofobruku, S.A. and Tor, Z.A., 2019. The implications of emotional intelligence on entrepreneurial performance: A discuss. South Asian Journal of Social Studies and Economics, 3(1), pp.1-13.
Page, S., Hartwell, H., Johns, N., Fyall, A., Ladkin, A. and Hemingway, A., 2017. Case study: Wellness, tourism and small business development in a UK coastal resort: Public engagement in practice. Tourism Management, 60, pp.466-477.
Purwatmini, N., Pranogyo, A.B., Sumampouw, R.W.J. And Arifin, A.L., 2021. Understanding Human Resource Management in Global Industry Practices: Systematic Review of International Publication. Journal of Contemporary Issues in Business & Government, 27(3).
Rather, R.A., Tehseen, S., Itoo, M.H. and Parrey, S.H., 2019. Customer brand identification, affective commitment, customer satisfaction, and brand trust as antecedents of customer behavioral intention of loyalty: An empirical study in the hospitality sector. Journal of Global Scholars of Marketing Science, 29(2), pp.196-217.
Ryu, S., 2020. The role of mixed methods in conducting design-based research. Educational Psychologist, 55(4), pp.232-243.
Sileyew, K.J., 2019. Research design and methodology. In Cyberspace (pp. 1-12). Rijeka: IntechOpen.
Sky.com, 2022, British Airways faces strike threat as ‘fire and re-hire’ deadline looms, viewed on 29/03/2022 <https://news.sky.com/story/british-airways-faces-strike-threat-as-fire-and-re-hire-deadline-looms-12037712>
Startuptalky.com, 2022, List of Most Famous Entrepreneurs in The World You Must Know About, viewed on 28/03/2022 <https://startuptalky.com/famous-entrepreneur-world/>
Stocker, F. and Abib, G., 2019. Risk Management in Born Globals: the Case of Brazilian Craft Breweries. Brazilian Business Review, 16(4), pp.334-349.
Stocker, F., Abib, G., Santos Jhunior, R. and Irigaray, H., 2021. Brazilian craft breweries and internationalization in the born global perspective. Revista de Gestão, 28(2), pp.163-178.
Stoecker, R. and Avila, E., 2020. From mixed methods to strategic research design. International Journal of Social Research Methodology, 24(6), pp.627-640.
Susanto, H. and Utami, C., 2020. Value Creation Networking Dimension Domination On Entrepreneurial Marketing Behavior: A Perspective Overview Of Companies Managed By Founders And Professionals. International Journal of Industrial Management, 5, pp.20-28.
Syaifuddin, S., 2021. The Influence of Corporate Communication Strategy and Customer Value Creation Toward Creation of Reputation (Case Study). Applied Information System and Management (AISM), 3(2), pp.93-100.
Thornton, M., 2020. Turning the Word Upside Down: How Cantillon Redefined the Entrepreneur. Quarterly Journal of Austrian Economics, 23(3-4), pp.265-280.
Turkina, E., 2017. The importance of networking to entrepreneurship: Montreal’s artificial intelligence cluster and its born-global firm Element AI. Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, 30(1), pp.1-8.
Vandenberg, R., 2011. Call for Papers: Feature Topic: Research Design. Organizational Research Methods, 14(3), pp.581-582.
Williams, M. and Moser, T., 2019. The art of coding and thematic exploration in qualitative research. International Management Review, 15(1), pp.45-55.
Yang, Y., Yang, X. and W. Doyle, B., 2013. The location strategy and firm value creation of Chinese multinationals. Multinational Business Review, 21(3), pp.232-256.


3 thoughts on ““Creating Value In International Business With Entrepreneurship Practices””